Types of Maintenance
Comparison of Maintenance types
Compare Different Types of Maintenance
Different types of maintenance exist because maintenance teams within different organizations have different budgets, equipment needs, and service level agreements with customers and internal departments like production.
Because so many types of maintenance exist, it’s hard to know which one is best for your organization. To narrow down your options, identify your maintenance budget and the acceptable level of unplanned downtime for each asset. Then, with this information, look through the different types of maintenance and select viable candidates.
If you’re having trouble understanding the pros and cons of different maintenance types, follow the links to the relevant comparison articles below. These articles compare two types of maintenance side by side. You’ll learn about how each maintenance type works, how much it costs to implement, how much money it saves, and how the pros and cons of one weigh against the other.
Preventive vs Predictive
Both preventive maintenance and predictive maintenance are designed to increase the reliability of assets and reduce the amount of reactivity to failures. The main difference between the two is that preventive maintenance is scheduled at regular intervals while predictive maintenance is scheduled as needed based on asset conditions.
Preventive vs Breakdown
Preventive maintenance and breakdown maintenance both seek to maintain and repair equipment but they have very different ways of doing this. In some ways, breakdown maintenance is the opposite of preventive maintenance because maintenance work doesn’t occur until a downtime event happens as opposed to avoiding downtime events by performing maintenance before they happen.
Preventive vs RCM
Both preventive maintenance (PM) and reliability centered maintenance (RCM) are designed to increase asset reliability and lifespan by creating a system of scheduled work. Both systems can be expensive in different ways. Preventive maintenance systems can be expensive due to their large scheduling needs while reliability centered maintenance systems often have a larger upfront cost.
Predictive vs Condition-Based
Predictive and condition-based maintenance are both maintenance types that occur before breakdowns happen. The primary difference between them is the way in which maintenance is measured. Predictive maintenance relies on precise formulas in addition to sensor measurements. Condition-based maintenance relies only on real-time sensor measurements.
Corrective vs Emergency
Both corrective maintenance and emergency maintenance happen in response to a fault or issue with equipment. The main difference between the two is the scale of that problem. Corrective maintenance is used for regular maintenance activities while emergency maintenance is used when an event causes safety issues or losses in production.
Planned vs Scheduled
While planned maintenance and scheduled maintenance sound like the same thing, some essential differences exist between them. Simply put, planned maintenance details how and what work will be completed; scheduled maintenance determines who will complete the work and when it will be completed.
Run to Failure vs Breakdown
Run to failure (RTF) maintenance and breakdown maintenance both aim to fix problems that occur when equipment breaks down, although the intent of each maintenance plan looks slightly different. In RTF maintenance, the maintenance team expects certain parts to break down and plans for that to occur. In breakdown maintenance, there is no planned strategy. The maintenance team simply responds and hopes they have everything they need to make the repair.
MAIN ARTICLES
Author of this quote
Run to Failure vs Breakdown Maintenance
Panels are a great tool to compare offers or to emphasize on key features. To compare products, use the inside col
Predictive vs Condition-Based Maintenance
Predictive vs Condition-Based Maintenance
Predictive and condition-based maintenance (PdM / CbM) are both maintenance types that occur before breakdowns happen. As such, they are both forms of proactive maintenance and are designed to increase reliability and decrease downtime.
The primary difference between them is the way in which maintenance is measured. Predictive maintenance relies on precise formulas in addition to sensor measurements (temperature, vibration, noise), and maintenance work is performed based on the analysis of these parameters. In this way, predictive maintenance is a very exact form of maintenance because it predicts future maintenance events.
On the other hand, condition-based maintenance relies only on real-time sensor measurements. Once a parameter reaches an unacceptable level, maintenance workers are dispatched. This means that condition-based maintenance systems perform work only in the moment it is needed.
Both predictive and condition-based maintenance can be expensive to initiate, though they both justify their upfront cost by saving money on downtime and equipment maintenance. Condition-based maintenance in particular can be expensive due to the cost of maintaining sensor devices, so it’s best used on critically important equipment.
Differences between predictive maintenance and condition-based maintenance
| Preventive Maintenance | Condition-based Maintenance | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Predictive maintenance (PdM) is work that is scheduled in the future based on analysis of sensor measurements and formulas. | Condition-based maintenance (CbM) is work that is performed at the exact moment when measured parameters reach unacceptable levels. |
| Workflow | 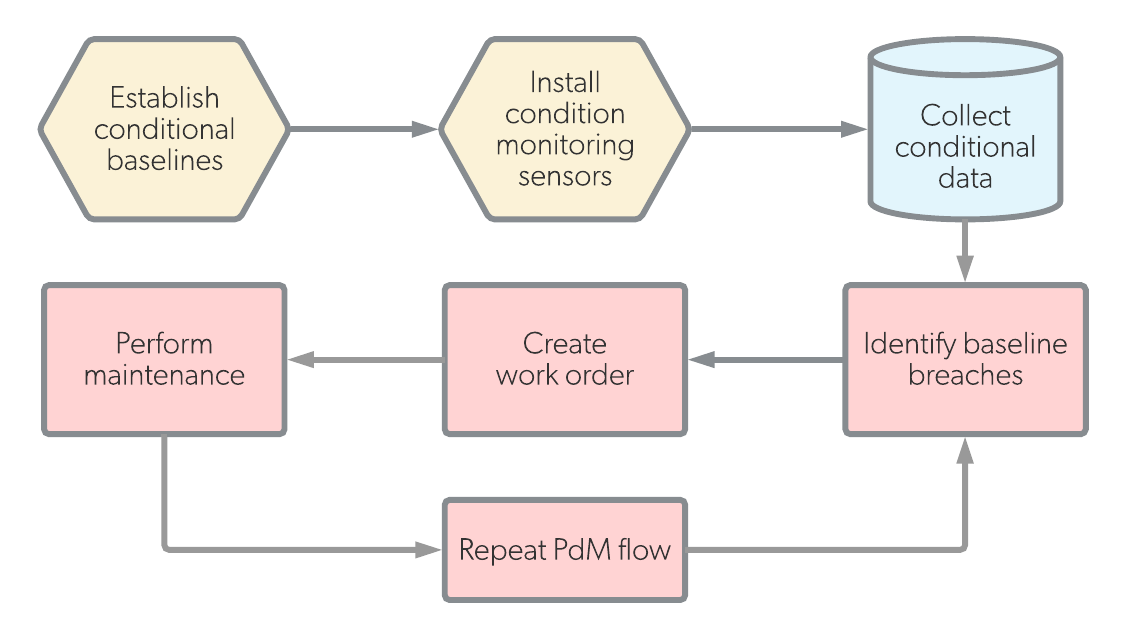 | 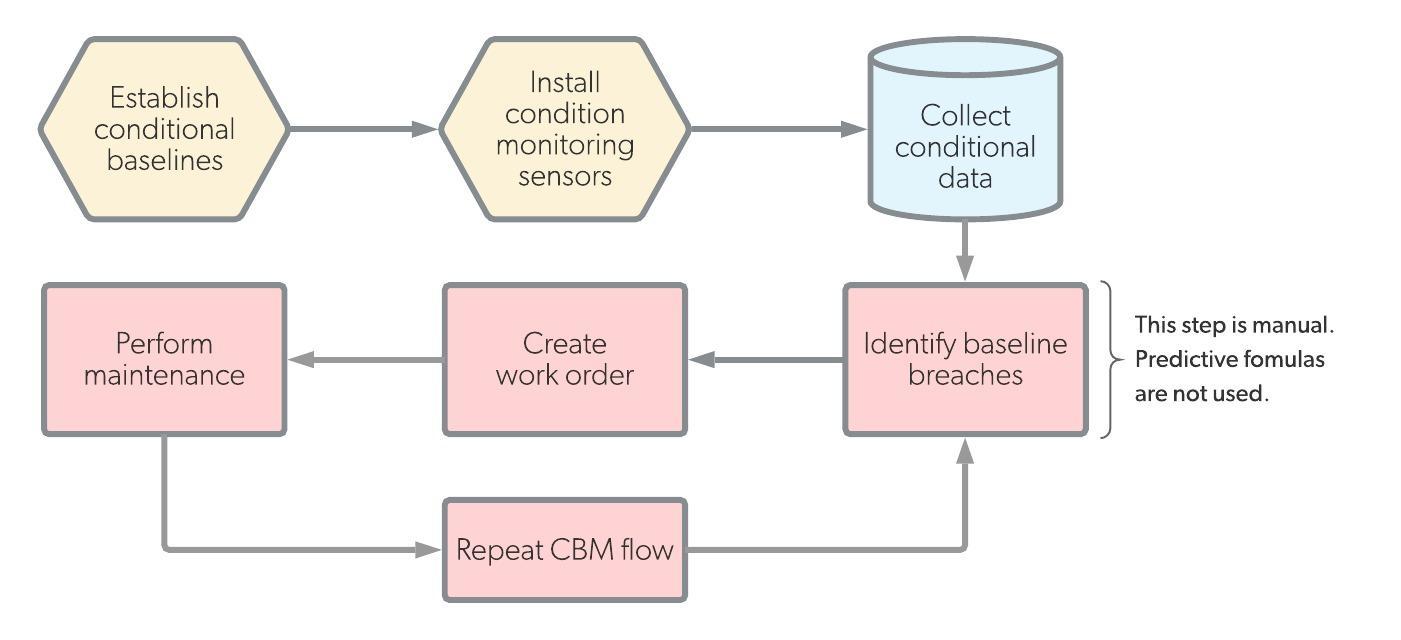 |
| Trigger | Predicted date | Measured parameter level |
| Cost | Medium/High | Medium/High (startup cost) |
| Cost Savings | 25% to 30% | Dependent on amount of equipment using CbM |
| Resources Needed |
|
|
| Pros |
|
|
| Cons |
|
|
| Use Case | An organization has assets with slow-speed bearings that frequently fail. Preventive maintenance is already in place but the organization suspects that assets are being over-greased. To perform maintenance with more precision, they use ultrasound analysis (good for slow-speed bearings). Now, work orders for greasing are only scheduled when certain ultrasound measurements are reached. | An organization needs to make sure that a critical piece of safety equipment can be maintained while it is running at load. One critical equipment parameter is the amount of vibration produced. The organization decides to implement CbM so that maintenance is performed only when vibrations begin to reach unsafe levels. This way, the safety equipment can be run constantly during maintenance and only receives maintenance when |
Feature Title
Panels are a great tool to compare offers or to emphasize on key features. To compare products, use the inside columns.
Feature Title
Panels are a great tool to compare offers or to emphasize on key features. To compare products, use the inside columns.

Leave a comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.